Sinan Rasiya Koya
I am on the job market and actively searching for positions. Please reach out regarding any potential opportunities in your team.
Thank you for visiting my website!
I'm Sinan (if you enjoy garlic naan, my name should be easy to remember 😉). Haven't
you intrigued by the Earth's marvels around? Its geological features, climate, and
ecosystems? I am!
This enthusiasm led me to pursue a PhD focusing on Hydrology. It all started at the Indian
Institute of Technology, Gandhinagar, where I received my bachelor's degree in Civil
Engineering. Currently, I'm a PhD candidate at the University of Nebraska-Lincoln, where
I am exploring Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Deep Learning applications in hydrology.
I study the hydrological extremes, like floods and droughts, and ways to improve predicting
them using AI. Over the past few years, I focused on snow-induced floods and droughts.
Outside of academia, I enjoy playing badminton and soccer. I am a philomath - learning
new things brings me joy. You can learn more about me from the links below.
Publications
Projects
Over the past years, I have been fortunate to be part of various impactful projects. This has been a great learning experience. Huge thanks to my mentors and colleagues who made these projects possible.
Global Composite Drought Indicator Hot Spot Early Warning and Information System

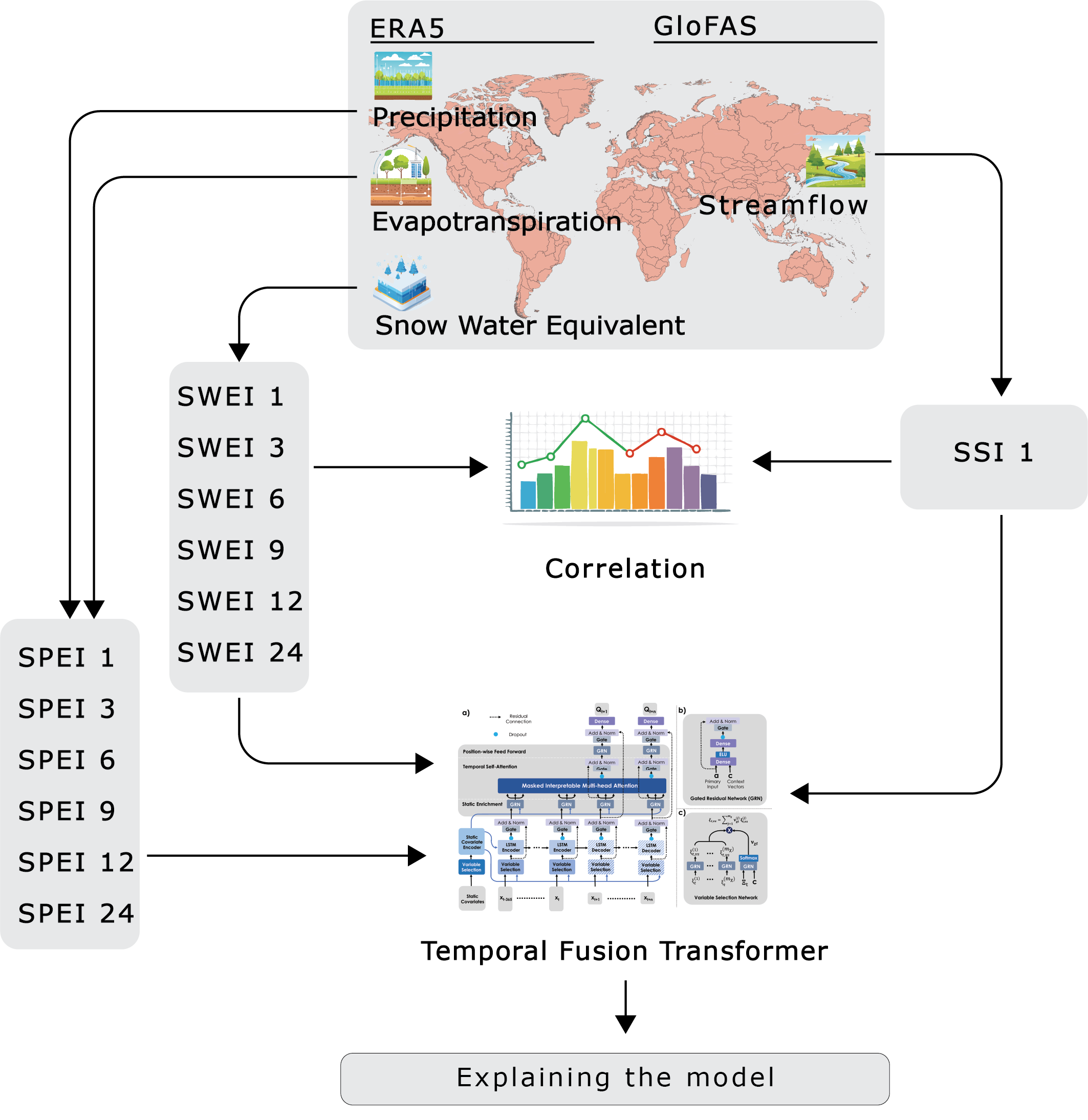
Streamflow Forecasting with Temporal Fusion Transformers

Prototype Flood Forecasting System for Nebraska

Impacts of Snow droughts and Associated Compound Events on Streamflow
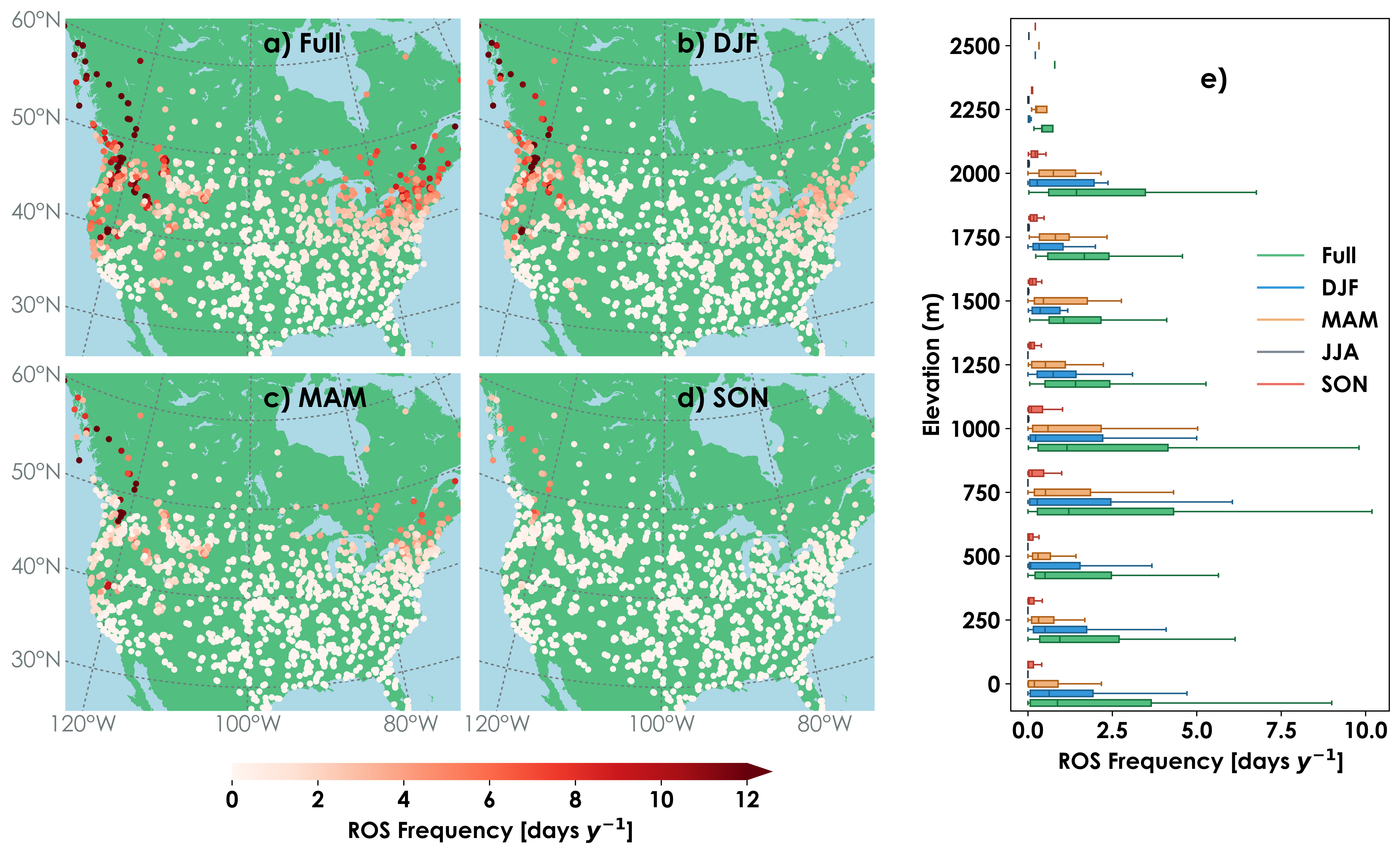
Drivers and Impacts of Rain-on-Snow in United States
Diffusion based rainfall runoff modeling

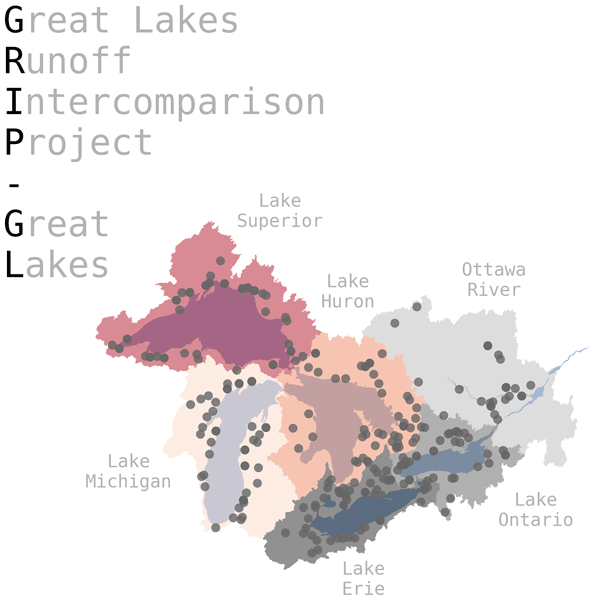
Great Lakes Runoff Intercomparison Project – Great Lakes (GRIP-GL)
Topology-based Flood Vulnerability of Global River Networks

Synthetic Global Precipitation Maps by Generative Adversarial Networks

